Task runners#
Task runners are a generic mechanism to execute tasks in a secure and performant way. They're used to execute user-provided JavaScript and Python code in the Code node.
This document describes how task runners work and how you can configure them.
Internal mode not recommended for production
Using internal mode in production environments can pose a security risk. For production deployments, use external mode to ensure proper isolation between n8n and task runner processes. Refer to Hardening task runners for additional security measures.
How it works#
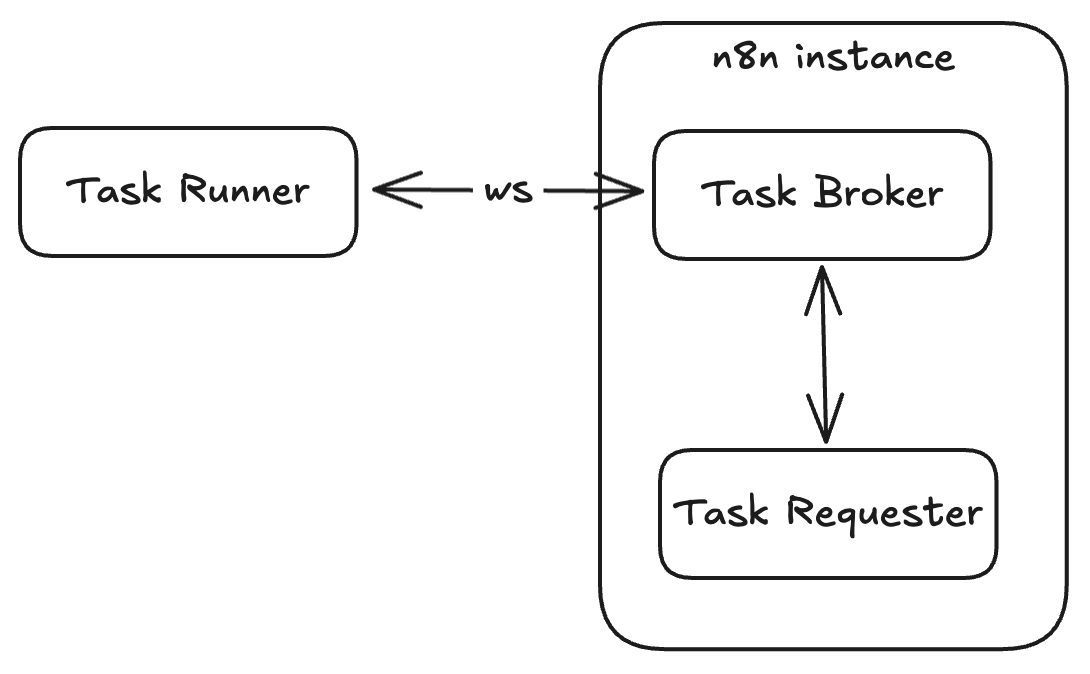
The task runner feature consists of these components: one or more task runners, a task broker, and a task requester.
Task runners connect to the task broker using a websocket connection. A task requester submits a task request to the broker where an available task runner can pick it up for execution.
The runner executes the task and submits the results to the task requester. The task broker coordinates communication between the runner and the requester.
The n8n instance (main and worker) acts as the broker. The Code node in this case is the task requester.
Task runner modes#
You can use task runners in two different modes: internal and external.
Internal mode#
In internal mode, the n8n instance launches the task runner as a child process. The n8n process monitors and manages the life cycle of the task runner. The task runner process shares the same uid and gid as n8n. This is not recommended for production.
External mode#
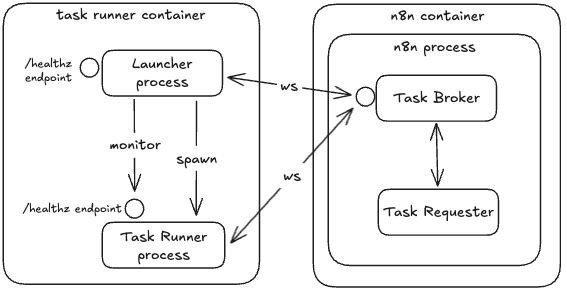
In external mode, a launcher application launches task runners on demand and manages their lifecycle. Typically, this means that next to n8n you add a sidecar container running the n8nio/runners image containing the launcher, the JS task runner and the Python task runner. This sidecar container is independent from the n8n instance.
When using Queue mode, each worker needs to have its own sidecar container for task runners.
In addition, if you haven't enabled offloading manual executions to workers (if you aren't setting OFFLOAD_MANUAL_EXECUTIONS_TO_WORKERS=true in your configuration), then your main instance will run manual executions and needs its own sidecar container for task runners as well. Please note that running n8n with offloading disabled isn't recommended for production.
Setting up external mode#
In external mode, you run the n8nio/runners image as a sidecar container next to n8n. Below you will find a docker compose as a reference. Keep in mind that the n8nio/runners image version must match that of the n8nio/n8n image, and the n8n version must be >=1.111.0.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | |
There are three layers of configuration: the n8n container, the runners container, and the launcher inside the runners container.
Configuring n8n container in external mode#
These are the main environment variables that you can set on the n8n container running in external mode:
| Environment variables | Description |
|---|---|
N8N_RUNNERS_ENABLED=true |
Enables task runners. |
N8N_RUNNERS_MODE=external |
Use task runners in external mode. |
N8N_RUNNERS_AUTH_TOKEN=<random secure shared secret> |
A shared secret task runners use to connect to the broker. |
N8N_RUNNERS_BROKER_LISTEN_ADDRESS=0.0.0.0 |
By default, the task broker only listens to localhost. When using multiple containers (for example, with Docker Compose), it needs to be able to accept external connections. |
For full list of environment variables see task runner environment variables.
Configuring runners container in external mode#
These are the main environment variables that you can set on the runners container running in external mode:
| Environment variables | Description |
|---|---|
N8N_RUNNERS_AUTH_TOKEN=<random secure shared secret> |
The shared secret the task runner uses to connect to the broker. |
N8N_RUNNERS_TASK_BROKER_URI=localhost:5679 |
The address of the task broker server within the n8n instance. |
N8N_RUNNERS_AUTO_SHUTDOWN_TIMEOUT=15 |
Number of seconds of inactivity to wait before shutting down the task runner process. The launcher will automatically start the runner again when there are new tasks to execute. Set to 0 to disable automatic shutdown. |
For full list of environment variables see task runner environment variables.
Configuring launcher in runners container in external mode#
The launcher reads environment variables from runners container environment, and performs the following actions:
- Passing environment variables from the launcher's own environment to all runners (
allowed-env) - Setting specific environment variables on specific runners (
env-overrides)
Which environment variables to pass and to set are defined in the launcher config file included in the runners image. This config file is located in the container at /etc/task-runners.json. To learn more about the launcher config file, refer to the Config file documentation.
The default launcher configuration file is locked down, but you can edit this file, for example, to allowlist first- or third-party modules. To customize the launcher configuration file, mount to this path:
1 | |
Adding extra dependencies#
1. Extend the n8nio/runners image#
You can extend the n8nio/runners image to add extra dependencies to the runners. You'll need n8nio/runners:1.121.0 or later to do this.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
You must also allowlist any first-party or third-party packages for use by the Code node. Do this by editing the configuration file n8n-task-runners.json to include the packages in your extended image.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | |
NODE_FUNCTION_ALLOW_BUILTIN: comma-separated list of allowed node builtin modules.NODE_FUNCTION_ALLOW_EXTERNAL: comma-separated list of allowed JS packages.N8N_RUNNERS_STDLIB_ALLOW: comma-separated list of allowed Python standard library packages.N8N_RUNNERS_EXTERNAL_ALLOW: comma-separated list of allowed Python packages.
2. Build your custom image#
For example, from the n8n repository root:
1 2 3 4 | |
3. Run the image#
For example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |